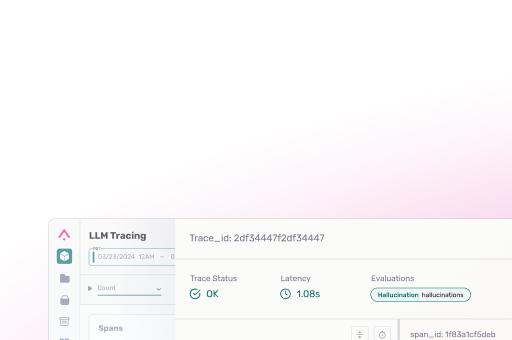
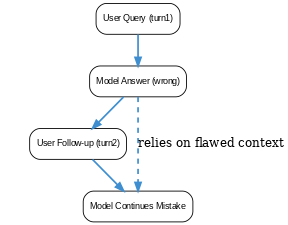
Large language models exhibit multi-turn performance degradation, often called semantic drift, during extended dialogues. When instructions are sharded across multiple turns instead of given in one prompt, models tend to make an early incorrect assumption and then compound those errors with each response – rarely recovering without resetting context. This failure mode means the model’s replies may progressively diverge from the user’s intent as the conversation continues. Research shows that even advanced open and closed-source LLMs suffer a 39% drop in reliability from single-turn to multi-turn settings. Mitigations include re-injecting all relevant information in a new prompt (to “refresh” context) rather than relying on the faulty dialogue history (paper).
What is Multi-Turn Semantic Drift?
Multi-Turn Semantic Drift
Bi-weekly AI Research Paper Readings
Stay on top of emerging trends and frameworks.