How to evaluate LLM performance across languages for complex cypher query generation using open source tools
As organizations expand globally, the need for multilingual AI systems becomes critical. But how do you evaluate whether your language model can handle business questions in non-English languages and still generate correct database queries? In this post, we’ll walk through building a comprehensive evaluation pipeline that tests multilingual text-to-Cypher generation using Phoenix for observability and evaluation tracking.
The Challenge: Non-English Database Query Generation
Imagine you’re building a chatbot that needs to answer business questions in multiple languages by querying a Neo4j graph database. Most training datasets for text-to-Cypher are in English, but your users speak Hindi, Tamil, Telugu, and other languages. Your evaluation pipeline needs to test:
- Translation: Convert English questions to target languages (Hindi, Tamil, Telugu)
- Query Generation: Generate syntactically correct Cypher queries from non-English questions
- End-to-End Accuracy: Ensure the translated question produces the same correct query as the original English
This is particularly challenging because you’re testing whether models can maintain technical accuracy (correct Cypher syntax and semantics) when processing non-English natural language inputs.
The Solution: A Phoenix-Powered Evaluation Framework
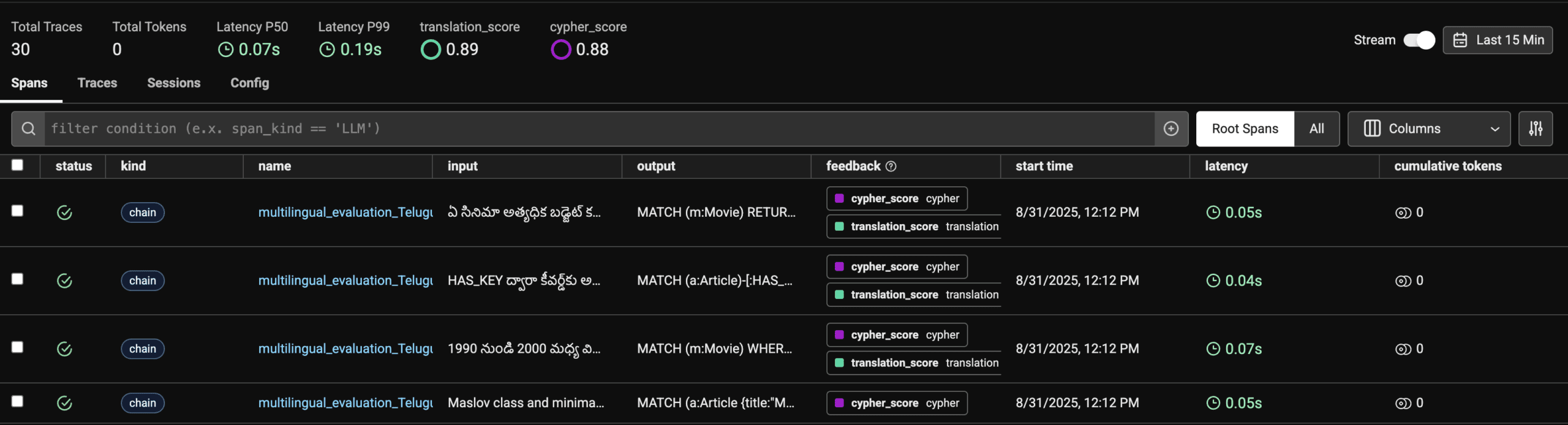
Our evaluation pipeline uses Phoenix to provide comprehensive observability across the entire multilingual evaluation process. Starting with English text-to-Cypher pairs from Neo4j’s dataset, we translate questions to target languages and test whether models can generate correct Cypher from non-English inputs. Here’s what makes this approach powerful:
- End-to-end tracking of English → translation → Cypher generation chains
- Translation quality assessment using back-translation and semantic similarity
- Cross-lingual Cypher accuracy comparison against English ground truth
- Rich metadata capture for detailed failure analysis
- Automated evaluation uploads for team collaboration
Setting Up the Evaluation Pipeline
1. Initialize Phoenix with DSPy Instrumentation
First, we set up Phoenix to capture all DSPy operations automatically:
from phoenix.otel import register
from openinference.instrumentation.dspy import DSPyInstrumentor
from phoenix.client import Client
def init_phoenix():
"""Initialize Phoenix UI for observability."""
PROJECT_NAME = "multilingual-cypher-eval"
tracer_provider = register(
project_name=PROJECT_NAME,
auto_instrument=True,
endpoint="http://0.0.0.0:6006/v1/traces"
)
tracer = tracer_provider.get_tracer(__name__)
DSPyInstrumentor().instrument()
client = Client(base_url="http://localhost:6006")
return tracer, client
2. Define DSPy Signatures for Evaluation Components
We create structured signatures for each component of our evaluation:
import dspy
class Translate(dspy.Signature):
"""Translates text into a target language."""
source_text = dspy.InputField(desc="The question in source language")
target_language = dspy.InputField(desc="Name of the language")
translated_text = dspy.OutputField(desc="The question in the target language.")
class GenerateCypher(dspy.Signature):
"""Generates a Cypher query from a question and schema."""
question = dspy.InputField(desc="Natural Language Question")
neo4j_schema = dspy.InputField(desc="Neo4J schema")
cypher_query = dspy.OutputField(desc="Generated Cypher Query")
class EvaluateCypherEquivalence(dspy.Signature):
"""Determines if two Cypher queries are functionally equivalent."""
ground_truth_query = dspy.InputField(desc="The correct/reference Cypher query")
generated_query = dspy.InputField(desc="The generated Cypher query to evaluate")
schema = dspy.InputField(desc="Neo4j database schema for context")
equivalence_category = dspy.OutputField(desc="One of: EQUIVALENT, PARTIALLY_CORRECT, INCORRECT, SYNTAX_ERROR")
reasoning = dspy.OutputField(desc="Brief explanation of the categorization")
3. Create the Full Pipeline Module
Our DSPy module orchestrates the complete evaluation flow:
class FullPipelineEvaluator(dspy.Module):
"""A DSPy module that translates English to target language, then generates Cypher."""
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.translator = dspy.Predict(Translate)
self.cypher_generator = dspy.Predict(GenerateCypher)
def forward(self, question, schema, target_language):
# Step 1: Translate English question to target language
t = self.translator(source_text=question, target_language=target_language)
# Step 2: Generate cypher from translated question
c = self.cypher_generator(question=t.translated_text, neo4j_schema=schema)
return dspy.Prediction(
translated_question=t.translated_text,
generated_query=c.cypher_query
)
Implementing Sophisticated Evaluation Metrics
Translation Quality Assessment
Since we’re translating FROM English TO target languages, we use back-translation to assess quality. This ensures our translated questions maintain the original semantic meaning:
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, util
def score_translation_quality(original_english_text, translated_text, back_translator, sentence_model):
"""Evaluates translation quality by back-translating to English and measuring semantic similarity."""
# Back-translate from target language to English
back_translation_result = back_translator(
source_text=translated_text,
target_language="English"
)
back_translated_text = back_translation_result.translated_text
# Compare original English with back-translated English using semantic similarity
embedding_original = sentence_model.encode(original_english_text, convert_to_tensor=True)
embedding_back_translated = sentence_model.encode(back_translated_text, convert_to_tensor=True)
similarity_score = util.pytorch_cos_sim(embedding_original, embedding_back_translated).item()
return {
"score": similarity_score,
"back_translated_text": back_translated_text
}
Cross-Lingual Cypher Query Evaluation
The key challenge: does the Cypher generated from the translated question match the ground truth from the original English question? We use an LLM judge to evaluate functional equivalence:
def compare_query_results_with_llm(ground_truth_query, generated_query, schema, cypher_judge):
"""Compare Cypher generated from translated question against English ground truth."""
result = cypher_judge(
ground_truth_query=ground_truth_query, # From original English dataset
generated_query=generated_query, # Generated from translated question
schema=schema
)
# Map categories to scores
category = result.equivalence_category.upper()
if category == "EQUIVALENT":
correct, score = True, 1.0
elif category == "PARTIALLY_CORRECT":
correct, score = None, 0.5 # Partial credit
elif category in ["INCORRECT", "SYNTAX_ERROR"]:
correct, score = False, 0.0
else:
correct, score = False, 0.0
return {
"correct": correct,
"category": category,
"score": score,
"reason": result.reasoning
}
Phoenix Integration: Rich Tracing and Evaluation Storage
Creating Custom Evaluation Spans
We create custom spans that capture the complete English → translation → Cypher flow:
def process_and_evaluate_sample(tracer, sample, evaluator, back_translator,
sentence_model, target_language, cypher_judge, sample_id):
"""Process one English sample: translate to target language, then generate Cypher."""
with tracer.start_as_current_span(
f"english_to_{target_language}_cypher_evaluation",
attributes={
"evaluation.original_english_question": sample['question']
[:200],
"evaluation.target_language": target_language,
"evaluation.sample_id": str(sample_id),
"evaluation.evaluation_type": "english_to_multilingual_cypher"
}
) as eval_span:
# Step 1: Translate English question to target language
# Step 2: Generate Cypher from translated question
pipeline_result = evaluator(
question=sample['question'], # Original English question
schema=sample['schema'],
target_language=target_language
)
# Evaluate translation quality (English → Target → English)
translation_score_result = score_translation_quality(
sample['question'], # Original English
pipeline_result.translated_question, # Translated to target language
back_translator,
sentence_model
)
# Evaluate if Cypher from translated question matches English ground truth
cypher_assessment = compare_query_results_with_llm(
sample['cypher'], # Ground truth from English dataset
pipeline_result.generated_query, # Generated from translated question
sample['schema'],
cypher_judge
)
# Set comprehensive evaluation attributes
evaluation_attrs = {
"evaluation.original_english_question": sample['question']
[:200],
"evaluation.translated_question": pipeline_result.translated_question[:200],
"evaluation.translation_quality_score": float(translation_score_result.get('score', 0.0)),
"evaluation.cypher_matches_english_ground_truth": cypher_assessment.get('correct'),
"evaluation.cypher_category": cypher_assessment.get('category', ''),
"evaluation.cypher_score": cypher_assessment.get('score', 0.0),
"evaluation.cross_lingual_success": (
cypher_assessment.get('correct') and
translation_score_result.get('score', 0.0) > 0.7
),
"evaluation.english_ground_truth_cypher": sample['cypher']
[:200],
"evaluation.generated_cypher_from_translation": pipeline_result.generated_query[:200]
}
eval_span.set_attributes(evaluation_attrs)
return pipeline_result, translation_score_result, cypher_assessment
Uploading Structured Evaluations
Phoenix’s annotation system allows us to upload structured evaluation scores for cross-lingual analysis:
# Upload translation quality scores (English → Target Language)
client.annotations.add_span_annotation(
annotation_name="translation_quality",
annotator_kind="LLM",
span_id=span_id,
label="english_to_target_translation",
score=float(translation_score.get('score', 0.0))
)
# Upload cross-lingual Cypher accuracy (Target Language → Cypher vs English Ground Truth)
client.annotations.add_span_annotation(
annotation_name="cross_lingual_cypher_accuracy",
annotator_kind="LLM",
span_id=span_id,
label="multilingual_cypher_generation",
score=cypher_assessment.get('score', 0.0),
metadata={
"category": cypher_assessment.get('category', ''),
"target_language": target_language,
"matches_english_ground_truth": cypher_assessment.get('correct')
}
)
Running the Complete Evaluation
Configuration and Model Setup
# Configuration
CONFIG = {
"dataset_size": 50,
"target_languages": ["Hindi", "Tamil", "Telugu"]
}
# Define models to evaluate
models_to_evaluate = [
{
"name": "openai/gpt-4",
"instance": dspy.LM(model='openai/gpt-4'),
"api_key_env": "OPENAI_API_KEY"
},
{
"name": "anthropic/claude-3-sonnet",
"instance": dspy.LM(model='anthropic/claude-3-sonnet'),
"api_key_env": "ANTHROPIC_API_KEY"
}
]
Main Evaluation Loop
def main():
"""Main evaluation function."""
# Initialize Phoenix
tracer, client = init_phoenix()
# Load dataset and resources
train_samples, sentence_model = load_resources()
all_results = []
for model_config in models_to_evaluate:
model_name = model_config['name']
llm_instance = model_config['instance']
# Configure DSPy with current model
dspy.settings.configure(lm=llm_instance)
# Initialize components
evaluator = FullPipelineEvaluator()
back_translator = dspy.Predict(Translate)
cypher_judge = dspy.Predict(EvaluateCypherEquivalence)
# Test each target language against English dataset
for target_language in CONFIG["target_languages"]:
for i, sample in enumerate(train_samples):
# Each sample contains: English question + ground truth Cypher
# We translate the English question, then generate Cypher from translation
pipeline_result, translation_score, cypher_assessment = \
process_and_evaluate_sample(
tracer=tracer,
sample=sample, # Contains English question + ground truth Cypher
evaluator=evaluator,
back_translator=back_translator,
sentence_model=sentence_model,
target_language=target_language,
cypher_judge=cypher_judge,
sample_id=i
)
# Store results for analysis
all_results.append({
"model_name": model_name,
"target_language": target_language,
"original_english_question": sample['question'],
"translated_question": pipeline_result.translated_question if pipeline_result else "",
"translation_quality_score": translation_score.get('score', 0.0),
"cypher_matches_english_ground_truth": cypher_assessment.get('correct'),
"cross_lingual_cypher_score": cypher_assessment.get('score', 0.0),
# ... additional metrics
})
Analyzing Results in Phoenix
Key Insights You Can Extract
- Translation Quality by Language: Which languages maintain semantic fidelity when translating from English?
- Cross-Lingual Query Accuracy: Can your model generate correct Cypher from non-English questions?
- Language-Specific Error Patterns: Do certain languages consistently produce specific types of Cypher errors?
- Model Robustness: Which models maintain accuracy across language barriers?
- Translation Impact on Technical Tasks: How much does translation quality affect downstream Cypher generation?
Phoenix UI Features for Analysis
- Filter spans by
evaluation.evaluation_type: "english_to_multilingual_cypher" - Compare translation quality scores across languages using semantic similarity
- Analyze cross-lingual Cypher accuracy against English ground truth
- Track end-to-end success rates for the complete English → Translation → Cypher pipeline
- Identify failure modes where translation succeeds but Cypher generation fails
Summary Performance Report
The evaluation automatically generates comprehensive reports:
# Overall performance by model
summary = df.groupby(['model_name']).agg(
samples_processed=('sample_id', 'count'),
avg_translation_quality=('translation_quality_score', 'mean'),
avg_cross_lingual_cypher_score=('cross_lingual_cypher_score', 'mean'),
cross_lingual_accuracy_pct=('cypher_matches_english_ground_truth', lambda x: (x == True).mean() * 100),
error_rate_pct=('has_error', lambda x: x.mean() * 100)
).round(2)
# Performance by target language
lang_summary = df.groupby(['target_language']).agg(
avg_translation_quality=('translation_quality_score', 'mean'),
avg_cross_lingual_cypher_score=('cross_lingual_cypher_score', 'mean'),
cross_lingual_accuracy_pct=('cypher_matches_english_ground_truth', lambda x: (x == True).mean() * 100)
).round(2)
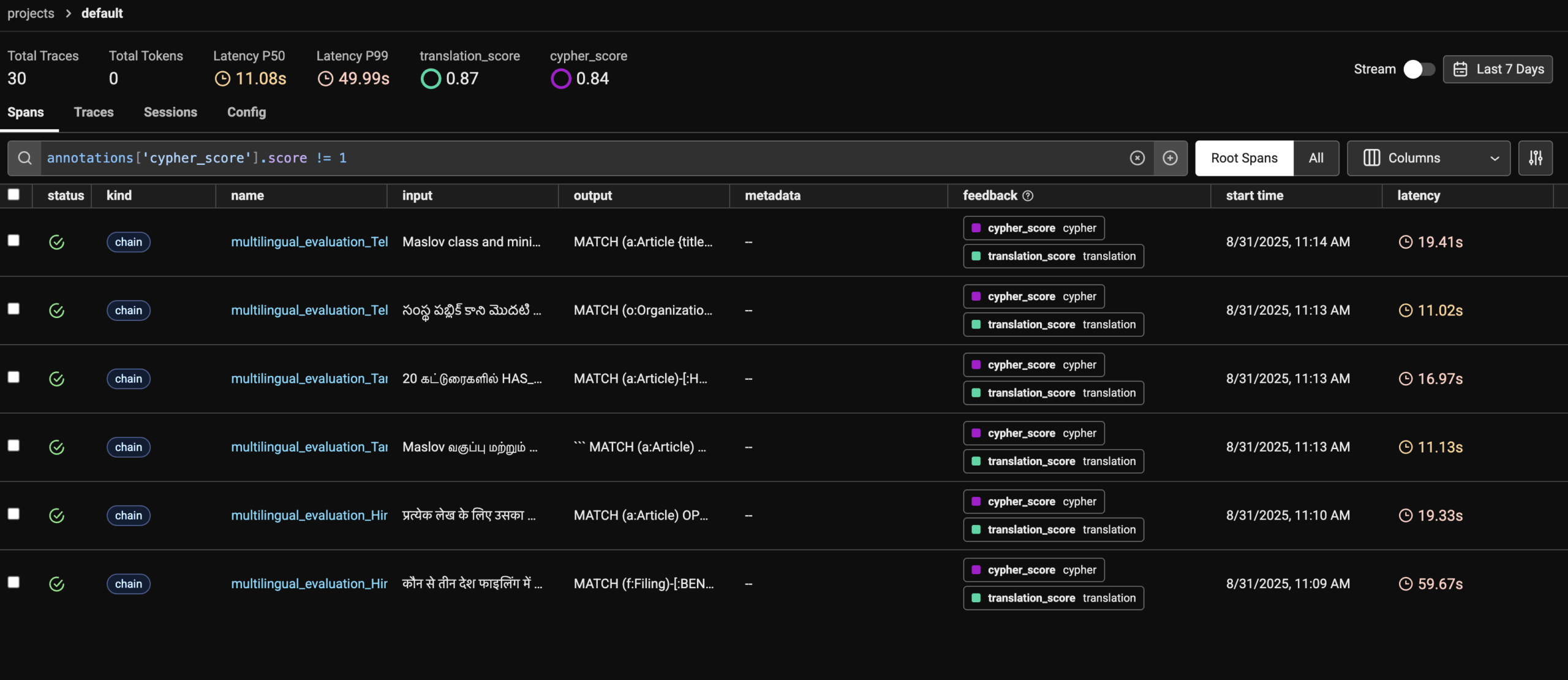
We can also use the Arize Phoenix dashboard to filter out all the evals where the Judge labelled the generated cypher “INCORRECT” Filter the spans using : annotations['cypher_score'].score != 1
Key Takeaways
This evaluation framework demonstrates several important principles for cross-lingual AI evaluation:
- End-to-End Cross-Lingual Testing: Don’t just test translation—test whether the entire pipeline maintains accuracy across languages
- Semantic Assessment Over Exact Matching: Use semantic similarity and LLM judges to evaluate functional equivalence
- Ground Truth Preservation: Compare outputs against the original English ground truth to measure cross-lingual consistency
- Rich Observability: Capture detailed context about translation quality and downstream task performance
- Language-Specific Analysis: Understand which languages are most challenging for your specific use case
The key insight: translation quality alone doesn’t guarantee task success. A model might translate perfectly but still fail to generate correct technical outputs like Cypher queries. This framework helps you identify where the pipeline breaks down.
Next Steps
- Extend to more languages: Add support for additional target languages
- Custom evaluation metrics: Implement domain-specific evaluation criteria
- A/B testing integration: Use Phoenix’s experiment tracking for model comparisons
- Production monitoring: Adapt this framework for ongoing production evaluation
Ready to build your own multilingual evaluation pipeline? Check out the complete code and start evaluating your models with Phoenix today!